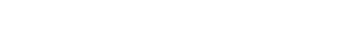
Tesla Leads As 25% of Countries Commit to Phasing Out Gas Vehicles: A Look at Each Country's Commitment
Nearly 25 percent of countries have announced plans for phasing out gas-powered vehicles. This international shift towards EVs is advantageous for Tesla, which continues to lead the electric car revolution. As countries enforce stricter emission standards and incentivize the adoption of EVs, Elon Musk and the Tesla team, who almost went broke 15 years ago, will continue to be in demand, setting the bar for a future of sustainable transportation.
United States Phase Out
The U.S., with California setting the ambitious goal of phasing out sales of new combustion engine vehicles by 2035. Several states, including Washington, Oregon, Connecticut, Massachusetts, New York, Vermont, and Delaware, align their vehicle standards with California, solidifying the nation's commitment to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Global Commitment
Not to be left behind, Canada is also championing the transition to EVs. However, the nation favours hybrids in its phase-out strategy, aiming for 2035.
Crossing the Atlantic, the European Union approved a law to ban combustion engine car sales in all member states by 2035. Despite some initial resistance from Germany and Italy, all 27 member states eventually backed the proposal, marking a significant step in reducing CO2 emissions across Europe. Countries like the Netherlands, Belgium's Flanders region, Sweden, Greece, and Slovenia are even more ambitious, targeting the end of gas-powered car sales between 2029 and 2030.

Norway is an electric mobility pioneer, with approximately 80 percent of new cars sold being fully electric. The country aims for 100 percent of new cars to be electric by 2025, showcasing a commitment that outshines many others.
Countries like China, Japan, and Singapore have proposed bans or are implementing 100% sales of zero-emission vehicles in Asia. Despite being one of the largest car markets, China, alongside Hong Kong and Macau, is steadfast in its commitment to phase out gas-powered vehicles, setting an example for the region.
Sri Lanka and Cape Verde are setting challenging goals. Sri Lanka aims for a full road ban for combustion engine cars, tuk-tuks, and motorcycles by 2040. Despite being a smaller country, Cape Verde internally set the goal to ban the sale of new combustion engine cars by 2035.
International Agreements
The global commitment to a cleaner, sustainable future was highlighted at the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, where multiple governments and companies signed the Glasgow Declaration, aiming for 100% zero-emission cars and vans by 2035 in leading markets and by 2040 globally.
In the wake of these global transitions, Tesla stands to gain substantially. The company's innovative technology, expanding production capabilities, and growing global presence position it perfectly to meet the rising demand for EVs. Tesla's diverse range of electric vehicles, from luxury to more affordable models, caters to a broad spectrum of consumers, ensuring its continued market dominance.
Infrastructure Advancement
The phase-out of gas-powered vehicles necessitates advancements in EV infrastructure. Tesla's ongoing investments in supercharging stations and battery technology place the company at the forefront of addressing the infrastructural challenges of widespread EV adoption. It recently turned on its 50,000 supercharger and opened the stations to allow non-Tesla to charge. Plus, the company opened up the patent for the North American Charging Standard, allowing other companies to use its advanced technology to further the ability to power up EVs.
The global shift towards electric vehicles is not just a trend but a commitment to a sustainable future. With countries worldwide, from the U.S. and Canada to Norway and Sri Lanka, phasing out gas-powered cars, Tesla's innovative approach and market readiness position it as a critical player in this electric revolution.
Here is a detailed breakdown of the commitments countries have made to a sustainable transportation future:
United States has an Executive Order mandating all new light-duty vehicles added to the government fleet to be 100% zero emissions by 2027, with the entire fleet of government-owned vehicles with ICE engines to be phased out and replaced with all-electric cars by 2035-2040.
The United Kingdom has a government plan to stop new non-electric and hybrid car sales by 2035 and new CO2-emitting lorry and bus sales by 2040.
Canada aims to phase out new light-duty vehicle sales of diesel, petrol, and non-electric cars by 2035 and aims for all light-duty vehicles to be electric by 2050.
Belgium plans to end tax deductions for diesel and petrol employee company cars by 2026 and stop new car and van sales in the Flanders region that run on these fuels by 2029.
Chile and the People's Republic of China are targeting 2035 to cease new vehicle sales of diesel and petrol cars.
Costa Rica has proposed to stop new light vehicle sales of diesel and petrol cars by 2050.
Denmark intends to halt new diesel and petrol vehicle sales by 2030, allowing hybrid vehicles until 2035.
Egypt has a government plan to cease new car sales of diesel, petrol, and non-electric vehicles by 2040.
According to a Bundesrat decision, Germany aims to stop new car sales of emitting vehicles by 2030.
Greece plans to halt new vehicle sales of emitting and non-electric cars by 2030.
Hong Kong (PRC) and Macau (PRC) aim to stop new private vehicle sales and registration of diesel and petrol cars by 2035.
Iceland is targeting 2030 to end the sale of new cars and vehicles that run exclusively on diesel or petrol, with some regional exceptions.
As a signatory of the Glasgow Declaration, India plans to halt new vehicle sales of petrol and diesel cars by 2040.
Indonesia has proposed to cease all motorcycle sales by 2040 and all car sales of diesel and petrol vehicles by 2050.
Israel aims to stop new car sales and imports of emitting, non-electric vehicles by 2030, although the citation is needed for confirmation.
Italy intends to stop new private vehicle sales by 2035 and recent commercial vehicle sales of emitting vehicles by 2040.
Japan plans to cease sales of new diesel- and petrol-only cars by 2035, with diesel and petrol-hybrid cars continuing to be sold indefinitely.
The Republic of Korea aims to halt new vehicle sales of petrol and diesel cars by 2035.
Malaysia plans to stop new vehicle sales emitting vehicles by 2050 as part of the Malaysia Net-Zero Emission by 2050 initiative.
The Netherlands is targeting 2030 to cease new passenger car sales of diesel and petrol vehicles, with commercial vehicles continuing to use these fuels until 2040.
Norway plans to stop all new passenger car sales of diesel and petrol vehicles by 2025, with commercial vehicles following suit by 2035.
Portugal has a government climate plan to stop new car sales of diesel and petrol vehicles by 2035.
Singapore has a phased plan starting in 2023, targeting zero tailpipe emission public sector vehicles by 2023, ceasing sales and registration of diesel-only cars and taxis by 2025, and implementing a complete phase-out of internal combustion engines by 2040.
Slovenia aims for new car registrations to have emissions below 50 g/km by 2031, allowing diesel and petrol if they meet this criterion.
Sweden has a coalition agreement to stop new car sales of diesel and petrol vehicles by 2030.
Taiwan plans a phased approach, stopping all bus and government-owned car use of diesel and petrol by 2030, all motorcycle sales by 2035, and all car sales by 2040.
Thailand has proposals to stop new car sales and registrations of diesel and petrol vehicles by 2035, although these are not yet effective.
Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Cambodia, Cape Verde, Croatia, Cyprus, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Finland, Ghana, The Holy See, Ireland, Kenya, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Mexico, Morocco, New Zealand, Paraguay, Poland, Rwanda, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine, and Uruguay have all signed the Glasgow Declaration, committing to stop the sales of new emitting vehicles by 2040.













![Tesla Autonomously Delivers Its First Vehicle to Customer — And It’s More Impressive Than Expected [VIDEO]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/img/containers/article_images/model-y-2025/newmodely_77.jpg/382e0312c769d0bb2e1234f7ac556fad/newmodely_77.jpg)

_300w.png)