Glamping with Tesla's Cybertruck and trailer concept
Glamping, a word that combines the terms, glamour and camping, refers to going to campgrounds but having the amenities normally present in a hotel.
Tesla has an interesting Cybertruck trailer concept. It's a large trailer about the size of a tiny house. It’s a nice looking trailer and it reflects the angularity and aerodynamic shape of the Cybertruck. In Cybertruck patents, Tesla shows the Cybertruck pulling a weight of 20,000 pounds, however the official Cybertruck specs say it can tow more than 14,000 pounds. I interpret that as a max weight of between 14,000 pounds and 15,000 pounds.
Now, remembering what we learned in high school physics, you’ll recall that how much weight a truck can tow has three components. The truck has to overcome rolling resistance, air resistance, and gravity. Now rolling resistance increases gradually depending on both the weight of the trailer and the speed you’re trying to tow it. It’s a linear increase. While there’s more rolling resistance at highway speeds than there is at parking lot speeds, it’s not all that much more.

Then there’s air resistance. That’s not related to the weight of the trailer at all. Air resistance is related only to the cross sectional area of the trailer, the aerodynamic shape of the trailer, and the speed of the tow. Air resistance increases as the square of the speed, so that’s a much more significant factor at highway speeds than at low speeds, but it has absolutely nothing to do with the weight of the trailer.
A few months ago, Ford came out with a publicity stunt involving a prototype electric Ford F-150 Lightning towing a million pounds of railroad cars when they were empty. Then they loaded one and a quarter million pounds of pickup trucks into the railroad cars, and the electric Ford towed all that, too (you can watch the full video below).
It was supposed to demonstrate something. All it demonstrated is that Ford likes to lie to people who don’t remember the physics they learned in high school.
The tow was done at slow speeds on steel rails with steel-wheeled railroad cars. Of all the land vehicles currently in use in the US, trains have the least rolling resistance. Maglev trains have less rolling resistance, but they’re not in use in the US. And anyway, maglev trains don’t roll. They float on a magnetic field. So all the electric Ford had to do was overcome a certain small rolling resistance. Admittedly, you or I would have been unable to start those train cars rolling by pulling or pushing by hand, but probably any pickup truck could have done it. It didn’t have to be a Ford.
The reason there’s a weight limitation for towing a trailer is that roads aren’t level. On hills, there are two considerations. The truck needs to be able to tow the trailer up any hill it might come across, and it has to be able to control the trailer when going down any hill it might come across. So if Tesla says the Cybertruck is rated for 14,000 pounds, then it really shouldn’t try towing 20,000 pounds even if that seems possible on level ground or mild hills. But there is a way around this limitation in the era of electric vehicles.
What I’m going to tell you does not come from Tesla, or any knowledgeable source. It comes strictly from my imagination so take it with a grain of salt.
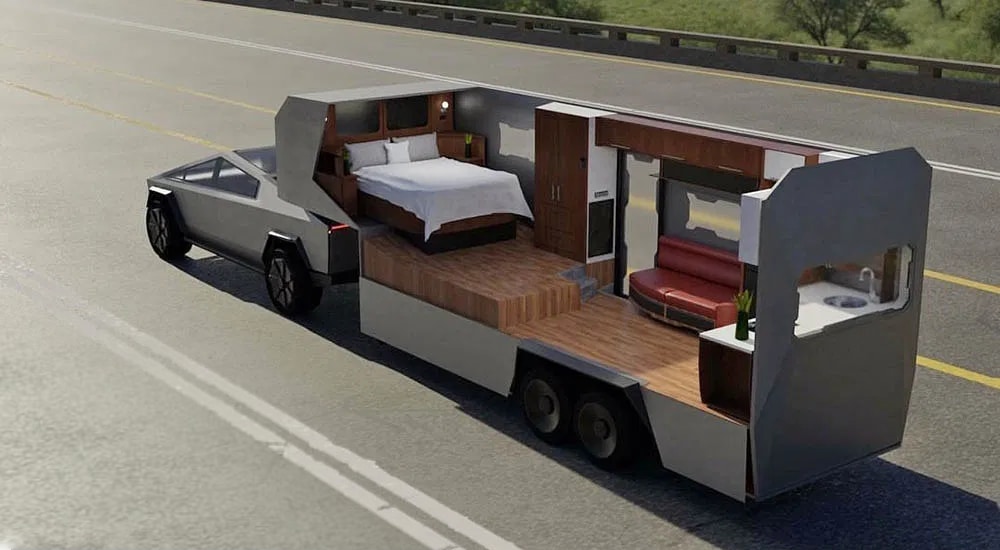

The way the Cybertruck can safely tow a load that’s higher than its rated maximum towing weight is if the trailer has its own batteries and its own electric motor(s). There would, of course, have to be coordination. The trailer would have to respond to the truck driver’s control input, but that’s not difficult to arrange. If the trailer had batteries and motor(s), the range between recharges would not be degraded by towing. If the trailer could be recharged separately from the Cybertruck by a second Supercharger stall, then the length of time to recharge wouldn’t be prolonged.
Now let’s talk about what the trailer could include. I looked up the weight of a standard 30-foot travel trailer. The weight averages around 5,800 pounds. So that leaves plenty of room for amenities. The trailer could expand, for example. It could expand upward when parked, or sideways. Lots of travel trailers do that. So instead of being 30 feet by 8 feet, it could be twice that. Perhaps it could expand sideways on both sides, That would make it 30 feet by 24 feet.
Add to that interior room, an extra roof to cover an outdoor patio, another 8 feet by 30 feet. Cover all that roof with solar panels, and you’d have lots of electricity while you were at the campground. Excess solar electricity created in the daytime would be stored in the trailer’s batteries at night.
Then there are other amenities. In addition to the normal water tanks for drinking, bathing, and other cleansing purposes, there could be a hot tub for two. That would hold 150 gallons of water, 600 pounds. Tesla is good at making heat pumps. Heat pumps can be used to heat or cool the trailer depending on the outside air temperature. If the trailer is parked near a stream or a lake, the heat pump might be able to exchange heat or cooling with the body of water if that would be more energy-efficient than exchanging heat or cooling with the outside air.
While traveling, there should be enough outside video cameras so that the driver would not have blind spots next to or behind the trailer. These should sync with the Cybertruck’s display screen.
The Ford F-150 Lightning has a helpful feature for hooking up the truck to a trailer. The driver first cranks up the trailer’s hitch to the proper height. Then he drives the truck to the front of the trailer so he can see the trailer hitch in the rear camera display. At that point, the truck itself backs up until the truck’s trailer hitch is properly aligned with the trailer’s hitch receptacle. Tesla should do that for the Cybertruck in a software update.
Finally, there should be Internet access via Starlink.










![Tesla Launches 'TeslaVision' Contest With Big Prizes — See Last Year’s Winner [VIDEO]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/img/containers/article_images/2025/tesla-vision.webp/0458df1c6ed085c427608f0cf762de64/tesla-vision.jpg)



![Tesla Officially Unveils New Model S and Model X: All the Changes [Photos]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/img/containers/article_images/2025/refresh_s_x_1.jpg/31a01e933ae496b97965b27db360f11b/refresh_s_x_1.jpg)




![Driverless Tesla Robotaxi Spotted on Camera in Austin [VIDEO]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/img/containers/article_images/robotaxi/robotaxi-public.webp/5ffd9ed0c2c7f9dbfee05decb1c19a2f/robotaxi-public.jpg)

![Andrej Karpathy considers returning to Tesla to work on Optimus [video]](https://www.notateslaapp.com/images/news/2022/karpathy-podcast_300w.jpg)